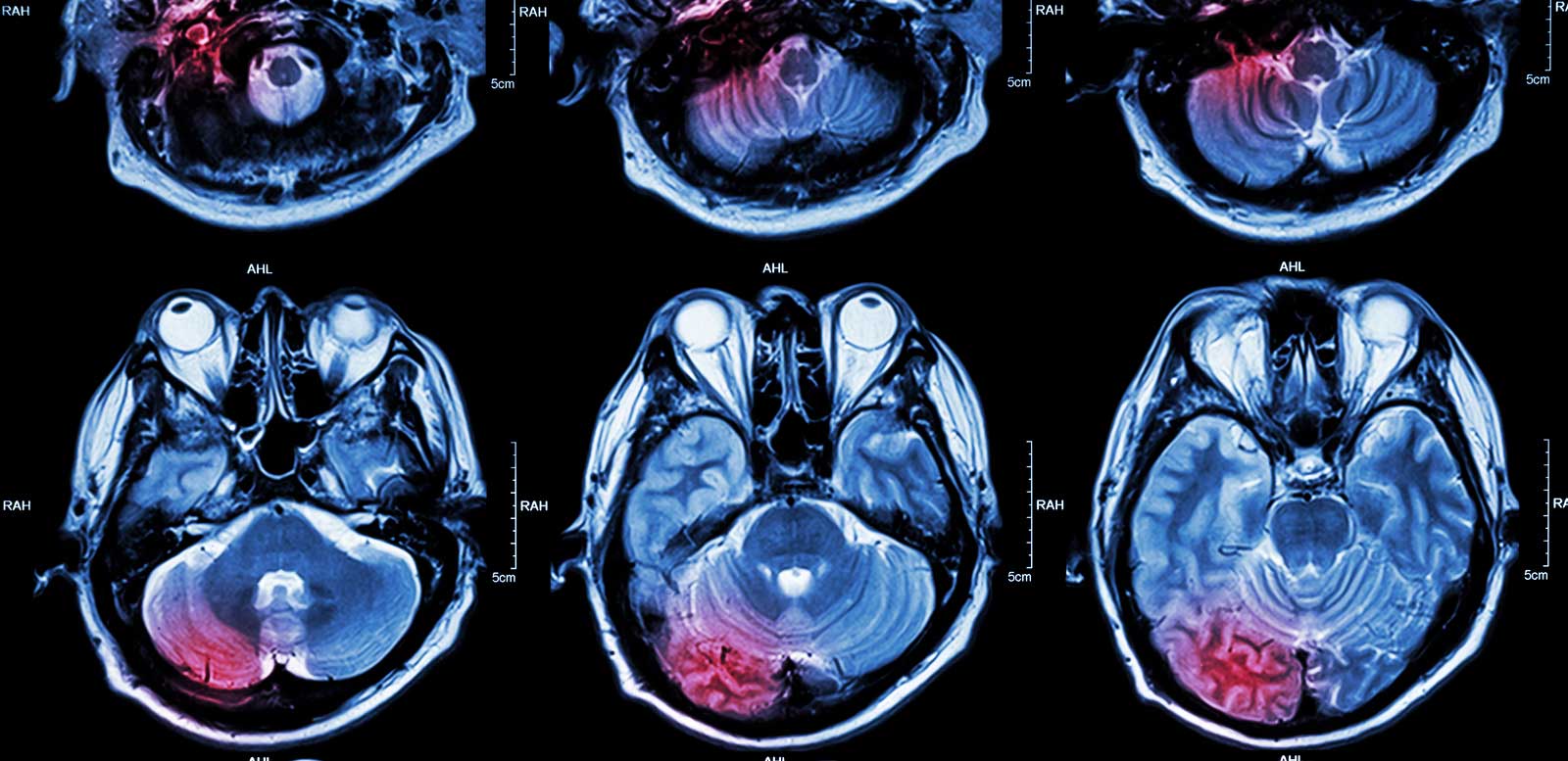
What is a Brain Tumor?
A growth or mass of abnormal cells in the brain or anywhere close to the brain is referred to as a brain tumor. There are different types of brain tumors.
- Benign Tumors – These are non cancerous brain tumors
- Malignant Tumors – These are cancerous tumors
- Primary Brain Tumors – These originate in the brain
- Metastatic / Secondary Tumors – The cancer starts in other parts of your body. Slowly it spreads to brain.
The rate at which a brain tumor grows may vary. Both location and the rate of growth of the tumor determines the manner in which it affects your nervous system functioning. The treatment of brain tumor treatment depends on the type of brain tumor, its size and exact location.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of a brain tumor vary greatly and depend on the brain tumor’s size, location and rate of growth.
General signs and symptoms caused by brain tumors may include:
- Onset of headaches
- Change in pattern of headaches
- Headaches that gradually become more frequent
- Headaches getting more severe with time (sometimes unbearable)
- Unexplained nausea
- Vomiting
- Problems with vision such as double vision, blurred vision, loss of peripheral vision etc.
- Gradual loss of sensation
- Loss of movement in an arm or a leg over time
- Difficulty with balance
- Difficulties with speech
- Confusion in everyday matters
- Change in behaviour or personality
- Seizures (this is to be observed in someone who had never had a history of seizures)
- Hearing problems
When to see your Doctor
It is important not to see your doctor right away if you you observe persistent signs and symptoms (listed above).
Causes of a Brain Tumor
Primary Brain Tumors – These originate in the brain or tissues adjacent to it (meninges), pituitary gland, cranial nerves, or pineal gland. Mutation of normal cells in their DNA results in these tumors. Mutations help growth and division of cancerous cells at fast rates leading to a mass of abnormal cells and ultimately a tumor. Primary brain tumors are less common as compared to secondary brain tumors.
There are different types of primary brain tumors. These include:
Acoustic Neuromas (schwannomas) – These benign tumors develop on nerves control balance and hearing.
Gliomas – Starts in the brain or spinal cord, including ependymoma, astrocytomas, glioblastomas, oligodendrogliomas and oligoastrocytomas.
Meningiomas – This is a tumor arising from membranes surrounding brain and spinal cord (meninges). Most of these tumors are noncancerous.
Pituitary Adenomas – Most of these are benign tumors that develop in the pituitary gland (base of the brain). The tumors tend to affect pituitary hormones impacting the whole body.
PNETs – The tumors are rare and cancerous. These start in embryonic (fetal) cells in the brain. The tumor may occur at any place in the brain.
Medulloblastomas – Common cancerous tumors in children, these originate in the lower back part of the brain. Slowly these spread through the spinal fluid. The tumors are not common among adults, but they may occur.
Germ Cell Tumors – These develop during childhood, especially at the site of testicles or ovaries. Sometimes these may even shift to other parts of the body, e.g. brain.
Craniopharyngiomas – The tumors are rare and noncancerous. Originating near the pituitary gland of the brain, the tumor may affect the pituitary gland and other structures nearby as it grows.
Secondary (metastatic) Brain Tumors
Secondary tumors result from cancer that does not originate in the brain. It starts elsewhere in the body and gradually spreads (metastasizes) to the brain. These tumors are more common in people with a history of cancer. A metastatic brain tumor may also the first sign of cancer that starts elsewhere in the body (in rare cases). Secondary brain tumors are more common than primary tumors.
Any cancer can spread to the brain, but the most common types include:
- Melanoma
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Colon cancer
- Kidney cancer
Risk Factors of Brain and Nervous System Tumors
The cause of most primary brain tumors is not clear. However, there are certain factors that may increase one’s vulnerability to brain tumor. These include:
Age – Brain tumor risk increases as one ages. Hence, brain tumors are more common in older adults.
Exposure to Radiation – People exposed to ionizing radiation are more vulnerable to brain tumor.
Family History – People with a family history of brain tumors / genetic syndromes are at increased risk of brain tumors.
Diagnosis
Doctor usually recommends a number of tests and procedures for diagnosis of Brain and Nervous System Tumors. These include:
Neurological Exam – This exam may include examining patient’s vision, balance, hearing, coordination, reflexes and strength. When difficulty is determined in one or more areas, it is an indication about the part of the brain being affected by a brain tumor.
Biopsy – This is a test to find tumor in other parts of the body. Doctors usually recommend collecting and testing of a sample of abnormal tissue (biopsy). The process is usually performed as part of an operation to remove tumor from the brain. Doctor may also use a needle for the same (stereotactic needle biopsy). It is effective for brain tumors in hard to reach areas or sensitive / risky areas within the brain. To perform a needle biopsy, the neurosurgeon drills a small hole into the skull through which a thin needle is inserted. The tissue is removed with a needle under the frequent guidance of MRI / CT scanning. The biopsy sample is examined in detail under a microscope. This helps in knowing if the sample is benign or cancerous. The surgeon can decide on a treatment using this information.
Imaging Tests – One of the most common of these tests is a Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) which is commonly used to diagnose brain tumors. A dye may be injected in some cases through a vein in the arm. Doctors use different specialized MRI scans components such as magnetic resonance spectroscopy, functional MRI and perfusion MRI to examine the tumor and plan treatment procedures. Some of the other commonly used imaging tests include positron emission tomography and (PET) computerized tomography (CT) scans.
Treatment Options for Brain and Nervous System Tumor
The treatment for a brain tumor will depend on the overall type, size and location of the tumor.
Surgery
The surgeon aims at removing the maximum amount of tumor as possible if it is located in an accessible place. Some tumors are small and easy to separate from the neighbouring brain tissue. Surgical removal of these tumors is possible. However, in other cases, tumors cannot be separated from surrounding tissue. Sometimes tumors are located near sensitive areas of the brain. This makes surgery risky. Under such condition, the doctor removes the maximum amount of tumor possible. Removal of a specific part of brain tumor helps patients minimize signs and symptoms.
Some of the risks of surgery include bleeding, infection, etc. Other risks depends on the location of the tumor is located. For instance, a tumor near the eyes can result in vision loss during surgery.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy makes use of high-energy beams like protons, X-rays etc to kill tumor cells. Usually, this therapy is given through a machine outside the body. This is also referred to as external beam radiation. Sometimes, the therapy may also be used via placing radiation inside the body very close to brain tumor. Also known as brachytherapy, it is very rarely used.
External beam radiation can either be focused on a single region of the brain (precisely where the tumor is located) or to the entire brain (whole-brain radiation). This kind of radiation is usually used to treat cancer that reached the brain from a different part of the body.
There are some side effects of radiation therapy such as irritation on scalp, fatigue, and headaches. This will depend on the type and dosage of radiation a patient receives.
Radiosurgery
Radiosurgery is designed to be accomplished in one treatment. Most patients are allowed to go home the same day. Varied types of technology are used in radiosurgery so as to deliver radiation with an aim to treat brain tumors. These may include linear accelerator (LINAC) or Gamma Knife.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
It is not a surgery in a literal sense. In fact, it makes use of multiple beams of radiation and aims at killing tumor cells through a very highly focused kind of radiation.
Chemotherapy
This therapy makes use of drugs to kill tumor cells. Patients are advised to these orally (pill form) or intravenously (injected into a vein). Temozolomide (Temodar) is the most common chemotherapy drug used to treat brain tumors. It is available as a pill. A variety of chemotherapy drugs are available. These may be used a per the specific condition and type of cancer the patient suffers from. There are some side effects of chemotherapy, depending on the dosage and type of medicine prescribed. Some of the common ones include vomiting, nausea, and hair loss.
Drug Therapy
Patients are given targeted drug treatments. The treatment focus on specific abnormalities which are known to be existing within cancer cells. Blocking of these abnormalities will help exterminate cancer cells.
Bevacizumab (Avastin) – This drug therapy is used to treat a specific type of brain cancer referred to as glioblastoma. The drug is given intravenously (through a vein). It works towards interfering the formation of new blood vessels. The blood supply to the tumor is cut off, killing the tumor cells.
Everolimus (Afinitor) – The drug is used to treat a benign brain tumor in individuals with genetic disorders known as tuberous sclerosis. This medication will block an enzyme in the body that promotes cancer cell growth.
Rehabilitation Post Treatment
Since brain tumors develop in different parts of the brain controlling speech, motor skills, thinking, vision etc, it is important that rehabilitation is added as an integral part of recovery. For this, your doctor may refer you to certain services that help. These include:
Speech Therapy – The specialists will help patients with speech difficulties.
Physical Therapy – This is known to help in regaining lost muscle strength or motor skills.
Occupational Therapy – This therapy will help patients get back to normal daily activities. The patient can get back to work with the help of this therapy.
Alternative Medicine Therapy
Much research has not been done on complementary and alternative brain tumor treatments. Also, none of the alternative treatments have proved positive to cure brain tumors. These treatments can help patients cope with a brain tumor and its treatment. It is important to talk to the doctor about these options.
Some of the complementary treatments that help brain tumor patients cope include:
- Acupuncture
- Music therapy
- Hypnosis
- Relaxation exercises
- Meditation / Yoga