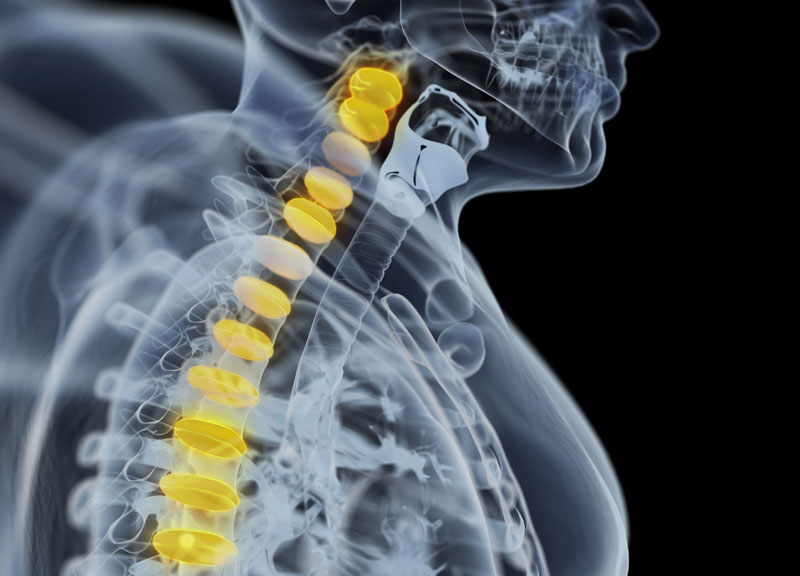
What is Disc Herniation?
The condition refers to an issue with one of the disks (rubbery cushions) between the vertebrae (the individual bones) that stack up to build your spine.
The Spinal Disc
It is similar to a jelly donut (small in size) comprising of a softer central region with tougher exterior. A herniated disc is also referred to as a ruptured or slipped disc. It occurs due to a part of soft jelly pushing out through a crack in the exterior.
The Effect
A herniated disk is known to irritate adjacent nerves leading to numbness, pain, or weakness in an arm or leg. Unfortunately, in most cases, people experience no symptoms at all. Also a lot of people with herniated disc may need surgery to treat the problem.
Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
Interestingly, one may have a herniated disc without even knowing about it. Sometimes, these are clearly shown on spinal images even in those without any symptoms. On the other hand, some herniated discs are quite painful.
Herniated Disc can be categorized as the following:
1. Lumbar Spinal Herniated Disc – Most of herniated disks occur in the lumbar spine (lower back)
2. Cervical Spinal Herniated Disc – These occur in the neck (cervical spine).
The most common signs and symptoms of a herniated disc include the following mentioned below:
Leg/ Arm Pain – When herniated disc occurs in the lower back, patients may feel intense pain in areas such as calves, buttocks, and thighs. The pain may also affect a part of the foot.
For neck herniated disc, the pain will get more intense on the shoulder and arm. The pain may shoot into the patient’s leg arm or leg, especially when he/she sneezes, coughs, etc. Pain is also felt while moving spine into certain positions.
Numbness or Tingling – Patients with herniated disk may experience numbness or tingling in the body, especially the part that serves affected nerves.
Weakness – Patients may experience weakness in muscles served by affected. This makes them trip, stumble, or even lose the ability to lift or hold items.
Seeing a Doctor
It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention when back or neck pain travels down the leg or arm. Patients must also report to the doctor when the pain is accompanied by a feeling of numbness, tingling or weakness.
Causes of Disc Herniation
Disc herniation is usually the result of gradual, age-related wear and tear. This is also referred to as disc degeneration. As you age, the spinal discs tend to lose a certain amount of water content. This makes these discs lose their natural flexibility, making them more vulnerable to tearing or rupturing with even a mild twist / strain.
Risk Factors
The following factors may make you more vulnerable to developing a herniated disc:
Overweight – Excess body weight may result in additional stress on the lower back disc.
Job – Those with physically demanding jobs, such as pulling, pushing things, labour are at a greater risk of back problems.
Activities – Pulling, repetitive lifting, pushing, twisting, and bending sideways may make you more prone to developing a herniated disk.
Genetics – Many tend to inherit a predisposition to develop disc herniation.
Complications of Disc Herniation
The spinal cord does not extend into the spinal canal’s lower part. It separates into a group of long nerve roots known as cauda equina right under the waist. Only under rare conditions, disk herniation compresses the whole of the cauda equina. Under such conditions, the patients require undergoing emergency surgery to avoid permanent weakness or paralysis. It is also crucial to seek emergency medical attention under the following conditions:
Worsening Symptoms – Any pain, weakness or numbness that increases to the point that it becomes impossible to perform your day to day activities should be immediately reported to the doctor.
Bladder or Bowel Dysfunction – People with cauda equina syndrome may suffer from incontinence. They face trouble urinating despite having a full bladder.
Saddle Anesthesia – This is a condition that results in progressive loss of sensation affecting the areas touching a saddle such as the back of legs, inner thighs, and the region around the rectum.
Preparing for an Appointment
One of the most important things you need to do is note down your symptoms. This will help the doctor assess your condition better and determine the best treatment / medication options. It is possible that your doctor may refer you to a doctor who specializes in the following fields:
- Physical medicine and rehabilitation
- Neurosurgery
- Orthopedic surgery
- Neurology
What to do before meeting a doctor?
It is important that you list out the following prior to meeting the doctor:
- The time you first started experiencing symptoms
- The action you were performing – pulling, lifting, pushing that triggered the symptoms.
- Any difficulty participating in activities.
- What improve your symptoms?
- What worsen your symptoms?
- What medications or supplements do you take?
Meeting a Doctor – What to Expect?
It is possible that your doctor might want to know about the following:
- Pain that travels into the arms or legs
- Any weakness or numbness in arms or legs
- Changes observed in bowel or bladder habits by the patient
- Coughing or sneezing worsening leg pain intensity
- Pain interferes with sleep or work?
Tests and Diagnosis Process
Physical Exam
The doctor prefers asking a number of questions when assessing the back for tenderness. The patient is asked to lie flat and then move the legs into different positions so as to help determine the exact of pain. The doctor may perform a neurological exam. This exam helps evaluate patient’s:
- Muscle strength
- Reflexes
- Walking ability
- Ability to feel very light touches, vibration, or pinpricks
Usually in most cases, a medical history assessment and a physical exam will suffice for a detailed diagnosis. When the doctor suspects another condition or wants to see which nerves are affected, one or more of the imaging tests listed below may be recommended.
Imaging Tests
Computerized tomography (CT scan) – The doctor uses a CT scanner aiming at taking a series of X-rays from varied directions. Thereafter, these are combined to create cross-sectional images of patient’s spinal column and adjacent structures.
X-rays – Usually plain X-rays are unable to detect herniated disks. However, doctors still perform it to rule out other causes of back pain, such as tumor, an infection, issues related to spinal alignment, broken bone problems etc.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – The medical practitioner will use a combination of radio waves and a strong magnetic field to create images of internal structures of a patient’s body. The test may also be conducted to confirm the exact location of the herniated disk. The doctor may also want to have a close view of the nerves affected by the condition.
Nerve Tests
Electromyograms and nerve conduction studies measure how well electrical impulses are moving along nerve tissue. This can help pinpoint the location of the nerve damage.
Myelogram
The process involves injecting of a dye is injected into the spinal fluid. Thereafter, X-rays are taken for detailed testing. They may also show some kind of pressure on the spinal cord or nerves. This is due to multiple herniated disks or any other condition the patient suffers from.
Treatment Options and Drugs
Traditional Treatment – This involves patients avoiding painful positions. The doctors will also suggest patients follow a set of planned exercise and pain-medication regimen. This helps relieve symptoms in most people with a herniated disk.
Medications for Disc Herniation
Over-the-counter Medications – These are prescribed when the patient suffers from mild to moderate pain. Some of the over-the-counter pain medications prescribed by doctors include ibuprofen such as Motrin IB and Advil. Naproxen like Aleve may also be prescribed according to the condition of the patient.
Drugs for Nerve Pain – The doctors may also prescribe specialized drugs for nerve pain such as the following:
- Gabapentin – Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant
- Pregabalin – Lyrica
- Duloxetine – Cymbalta
- Tramadol – Ultram
- Amitriptyline
These drugs can cause mild side effects.
Narcotics – When pain does not show any significant improvement with over-the-counter medications, the doctor may prescribe narcotics. Some of the common narcotics prescribed include oxycodone-acetaminophen combination such as Oxycontin, Percocet, etc. Codeine may also be prescribed. These drugs may cause certain side effects such as nausea, sedation, confusion and constipation.
Muscle Relaxants – Muscle relaxants are usually prescribed for muscle spasms. Some of the common side effects faced by patients include sedation and dizziness.
Cortisone Injections – These are inflammation-suppressing injections injected directly into the area around the spinal nerves. The doctors take the help of spinal imaging to guide the needle appropriately and more safely.
Oral Steroids – Doctors may recommend a course of oral steroids occasionally to minimize swelling and inflammation.
Therapy for Treating Disc Herniation
Most physical therapists will educate their patients about positions and exercises precisely designed to reduce the herniated disk pain. They usually recommend the following therapies to help patients:
- Heat / ice
- Ultrasound
- Traction
- Electrical stimulation
- Short-term bracing for lower back and the neck
Surgical Treatment
Only a very small number of patients require surgery. The doctor may suggest surgery only if all conservative treatments fail to improve symptoms in 6-8 weeks. In case, the patient continues to experience the following symptoms despite traditional treatment, the doctor will recommend surgery:
- Numbness
- Weakness
- Difficulty standing
- Problems in walking
- Loss of bladder control
- Loss over bowel control
In many cases, surgeons can remove just the protruding portion of the disk. Rarely, however, the entire disk must be removed. In these cases, the vertebrae may need to be fused together with metal hardware to provide spinal stability. Rarely, your surgeon may suggest the implantation of an artificial disk.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Making certain lifestyle changes and following simple home remedies will help you get relief from pain. Here’s what you can do to tackle the pain and enjoy life:
Pain Relievers – Many over-the-counter medications are prescribed for dealing with pain arising from a herniated disc. These include:
– Ibuprofen: Motrin IB, Advil
– Naproxen: Aleve
Heat / Cold Therapy – This is a great way to deal with pain. Cold packs are recommended for relieving pain and inflammation. After a few days, try and switch over to gentle heat. This will provide you with significant relief and comfort from pain.
Limit Bed Rest – Have you been resting too much? Well, this is something you need to avoid at any cost. Although some amount of rest is important to deal with the pain, excess of bed rest may result in stiff joints and weak muscles. The condition will complicate your recovery process. The best thing to do is rest in a comfortable position for around 30 minutes. Go for a short walk or indulge in some work. The idea is to get out of bed. Also try to avoid activities that may worsen your pain during the healing process.
Coping and Support By Premier Brain & Spine
Bearing pain is tough. It can affect one’s mental and physical wellbeing. Those dealing with recurring herniated disks or other kinds of back problems are also vulnerable to problems associated with psychological and emotional health.
These tips mentioned below may help you cope with herniated disk pain:
What Triggers It? – It is important to identify pain triggers. There are some activities or behaviours that worsen pain. Knowing these will help you avoid or limit them. This is important to increase the quality of life.
Stress Management – Did you know stress intensifies pain? To avoid stress (professional or personal life), practise deep-breathing exercises and other relaxation techniques such as yoga especially when the stress level goes up.
Meet a Counselor – It is important that you discuss your problems with mental health counsellor. This is very helpful in recognizing some of the unrealistic expectations and beliefs that you have about yourself. It is true that chronic pain hurts and affects the way you lead a life. However, it is also possible to lead a happy and stress free life by changing the way you feel about the pain.
Prevention Practises
There are a number of precautionary methods you can use to prevent a herniated disk:
Healthy Body Weight – Maintaining a healthy body weight is very helpful in preventing herniated disk. Remember that excess weight tends to exert more pressure on the disks and the spine, increasing their vulnerability to herniation.
Exercise – Most people do not take workout seriously. In fact, they don’t consider it as a crucial part of their lifestyle. Daily exercises will help you strengthen trunk muscles and facilitate spinal stability and provides it the support needed.
Posture – It is very important to maintain good posture. This helps with minimizing the pressure on the disks and spine. You must keep your back straight and aligned always (especially when sitting for long periods). Watch out your posture when lifting heavy objects. Focus on the leg work and avoid any strain on your back.